JavaScript 环境记录理解(ECMA2024)
TIP
记录个人理解,大佬们不喜勿喷,感谢
什么是环境记录
Environment Record is a specification type used to define the association of Identifiers to specific variables and functions, based upon the lexical nesting structure of ECMAScript code.
环境记录(Environment Record)是一种规范类型,用于根据 ECMAScript 代码的词法嵌套结构,定义标识符与特定变量和函数的关联。
核心:定义了标识符(var、let、const、function...定义的变量名)与特定变量 & 函数 的关联(映射关系)
标识符:
在 JS 中所有的可以由我们自主命名的都可以称为是标识符
例如:变量名、函数名、属性名都属于标识符
环境记录的创建
Usually an Environment Record is associated with some specific syntactic structure of ECMAScript code such as a FunctionDeclaration, a BlockStatement, or a Catch clause of a TryStatement. Each time such code is evaluated, a new Environment Record is created to record the identifier bindings that are created by that code.
通常,环境记录与 ECMAScript 代码的某些特定语法结构相关联,例如函数声明 FunctionDeclaration、BlockStatement 或 TryStatement 的 Catch 子句。 每次评估此类代码时,都会创建一个新的环境记录,以记录该代码创建的标识符绑定。
核心:当遇到以下代码时,就会创建一个新的环境记录。
- 函数声明 Script
- {}块语句
- try catch 的 catch 块
环境记录的[[outerEnv]]
Every Environment Record has an [[OuterEnv]] field, which is either null or a reference to an outer Environment Record. This is used to model the logical nesting of Environment Record values.
每个环境记录都有一个[[OuterEnv]]字段,该字段要么为空,要么是对外部环境记录的引用。 它用于模拟环境记录值的逻辑嵌套。
每个环境记录都有一个[[OuterEnv]]字段
**全局环境记录 OuterEnv 为 null **
当前环境记录可以访问到最近的外部环境记录
环境记录的分类
Environment Records can be thought of as existing in a simple object-oriented hierarchy where Environment Record is an abstract class with three concrete subclasses: Declarative Environment Record, Object Environment Record, and Global Environment Record. Function Environment Records and Module Environment Records are subclasses of Declarative Environment Record.
环境记录可以被视为存在于一个简单的面向对象层次结构中,其中环境记录是一个抽象类,有三个具体的子类: 声明环境记录、对象环境记录和全局环境记录。 函数环境记录和模块环境记录是声明式环境记录的子类。
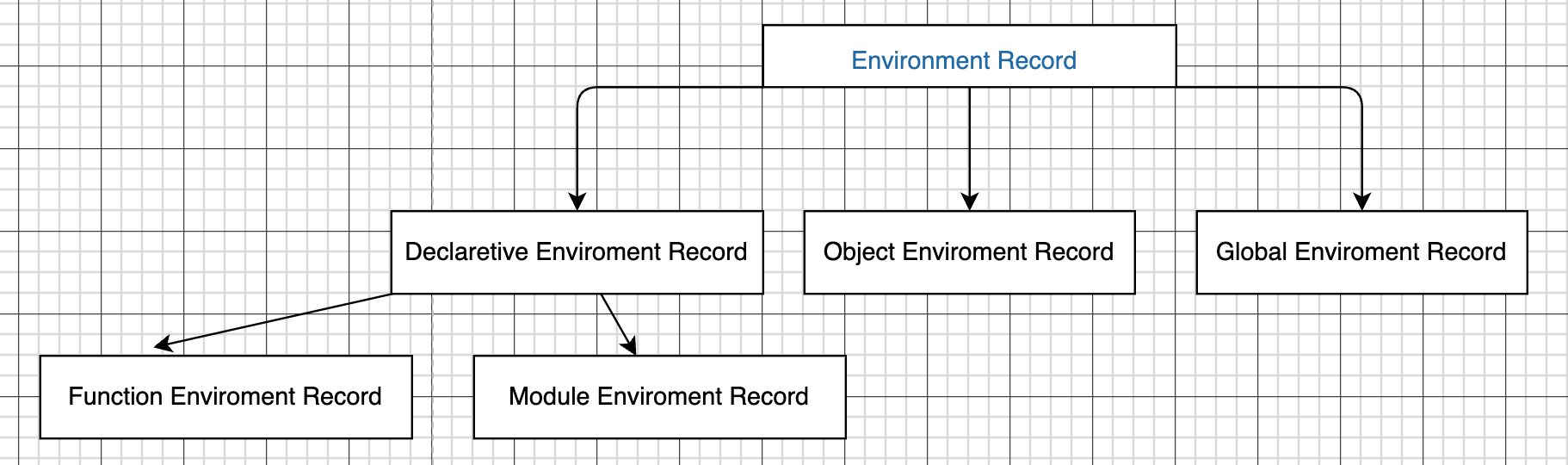
声明式环境记录
A Declarative Environment Record is used to define the effect of ECMAScript language syntactic elements such as FunctionDeclarations, VariableDeclarations, and Catch clauses that directly associate identifier bindings with ECMAScript language values.
在 ECMAScript 规范中,声明式环境记录(Declarative Environment Record) 用于描述某些语法结构(如
FunctionDeclaration、VariableDeclaration和catch子句)的执行效果。它的主要功能是直接将标识符绑定到 ECMAScript 语言中的值上。换句话说,声明式环境记录是为标识符(如变量名或函数名)提供存储位置的一个抽象结构,并负责管理它们的生命周期和作用域。Each Declarative Environment Record is associated with an ECMAScript program scope containing variable, constant, let, class, module, import, and/or function declarations. A Declarative Environment Record binds the set of identifiers defined by the declarations contained within its scope.
每个声明式环境记录都与包含var、const、let、类、模块、导入和/或函数声明的 ECMAScript 程序作用域相关联。 声明式环境记录绑定了其作用域中包含的声明所定义的标识符集。
存储内容
包含变量、常量、let、const、函数、类的声明。
应用场景
- 用于管理函数或块级作用域内的标识符。
特点
- 标识符和值直接绑定在环境记录中,而不是依赖于 JavaScript 对象。
- 支持块级作用域(
let和const)。 - 为函数作用域、块作用域等提供支持。
代码示例
function foo() {
let a = 10; // 'a' 是 foo 的声明式环境记录中的绑定
const b = 20; // 'b' 同样存储在声明式环境记录中
{
let c = 30; // 'c' 存储在块级作用域的声明式环境记录中
}
console.log(a, b); // 'c' 已经超出了其环境记录的作用域
}
foo();对象式环境记录(Object Environment Record)
An Object Environment Record is used to define the effect of ECMAScript elements such as WithStatement that associate identifier bindings with the properties of some object.
对象环境记录用于定义 ECMAScript 元素(如 WithStatement)的效果,这些元素将标识符绑定与某些对象的属性相关联。
Each Object Environment Record is associated with an object called its binding object. An Object Environment Record binds the set of string identifier names that directly correspond to the property names of its binding object. Property keys that are not strings in the form of an IdentifierName are not included in the set of bound identifiers.
每个对象环境记录都与其绑定对象相关联。 对象环境记录绑定与其绑定对象的属性名称直接对应的字符串标识符名称集。 非字符串形式标识符名称的属性键不包含在绑定标识符集合中。
存储内容
基于 JS 对象的绑定
特点
使用对象来存储绑定信息。 with
代码示例
const obj = { a: 10, b: 20 };
with (obj) {
console.log(a); // 输出 10
console.log(b); // 输出 20
}- 在上面的代码中,
with (obj)会创建一个对象环境记录,a和b(标识符)被绑定到obj的属性a和b(对象的属性)。 - 在
with语句块内,访问a和b会首先查找该对象的属性,因此它们的值被正确地访问。
全局环境记录(Global Environment Record)
A Global Environment Record is used for Script global declarations. It does not have an outer environment; its [[OuterEnv]] is null. It may be prepopulated with identifier bindings and it includes an associated global object whose properties provide some of the global environment's identifier bindings. As ECMAScript code is executed, additional properties may be added to the global object and the initial properties may be modified.
全局环境记录用于脚本全局声明。 它没有外部环境;其[[OuterEnv]]为空。 它可以预先填充标识符绑定,并包含一个关联的全局对象,其属性提供了全局环境的部分标识符绑定。 在执行 ECMAScript 代码时,可以向全局对象添加其他属性,也可以修改初始属性。
A Global Environment Record is used to represent the outer most scope that is shared by all of the ECMAScript Script elements that are processed in a common realm. A Global Environment Record provides the bindings for built-in globals (clause 19), properties of the global object, and for all top-level declarations (8.2.9, 8.2.11) that occur within a Script.
全局环境记录(Global Environment Record)用于表示在共同领域中处理的所有 ECMAScript 脚本元素共享的最外部范围。 全局环境记录(Global Environment Record)为内置的全局对象(globals/window)、全局对象的属性(properties of the global object)以及脚本中出现的所有顶层声明(8.2.9、8.2.11)提供了绑定。全局环境记录在逻辑上是一个单独的记录,但它是一个包含对象环境记录和声明环境记录的复合 记录。 对象环境记录的基本对象是关联的 "境界记录 "的全局对象。 该全局对象是全局环境记录的 GetThisBinding 具体方法返回的值。 全局环境记录(Global Environment Record)的对象环境记录(Object Environment Record)组件包含所有内置全局对象的绑定,以及全局代码中包含的函数声明(FunctionDeclaration)、生成器声明(GeneratorDeclaration)、异步函数声明(AsyncFunctionDeclaration)、异步生成器声明(AsyncGeneratorDeclaration)或变量声明(VariableStatement)所引入的所有绑定。 全局代码中所有其他 ECMAScript 声明的绑定都包含在全局环境记录(Global Environment Record)的声明环境记录(Declarative Environment Record)组件中。
存储内容
将全局变量和全局对象结合。将对象环境记录&声明式环境记录结合
特点
既包括声明式部分(let、const),也包括对象式部分(var、全局对象属性)。
代码示例理解
// 全局环境记录对象,整合了对象环境记录和声明式环境记录
GlobalEnvironmentRecord {
// 对象环境记录部分
objectEnvironmentRecord: {
baseObject: window, // 以浏览器环境为例,关联全局对象window
bindings: {
// 用于存储内置全局属性、var声明变量、函数声明等相关绑定信息
}
},
// 声明式环境记录部分
declarativeEnvironmentRecord: {
bindings: {
// 用于存储let、const等声明相关绑定信息
}
},
// 外部词法环境引用,全局环境下通常为null
outerLexicalEnvironment: null
}TIP
只是在全局环境记录中,声明式环境记录记录了 let const 声明的标识符的绑定,并不是说,声明式环境记录只能记录 let const 的绑定。究其原因,是在全局环境记录的特殊性,全局代码中的声明都在全局对象中
函数环境记录
A Function Environment Record corresponds to the invocation of an ECMAScript function object, and contains bindings for the top-level declarations within that function. It may establish a new
thisbinding. It also captures the state necessary to supportsupermethod invocations.函数环境记录与 ECMAScript 函数对象的**调用相对应,并包含该函数中顶层声明**的绑定。 它可以建立新的 this 绑定。 它还能捕捉支持 super 方法调用所需的状态
A Function Environment Record is a Declarative Environment Record that is used to represent the top-level scope of a function and, if the function is not an ArrowFunction, provides a
thisbinding. If a function is not an ArrowFunction function and referencessuper, its Function Environment Record also contains the state that is used to performsupermethod invocations from within the function.函数环境记录(Function Environment Record)是一种声明式环境记录,用于表示函数的顶层作用域,如果函数不是 ArrowFunction(箭头函数) ,则提供 this 绑定。 如果函数不是 ArrowFunction 并引用了 super,那么其函数环境记录还包含用于在函数内部执行 super 方法调用的状态。
理解:
函数执行时创建该函数的函数环境记录
特点
- 参数和局部变量:存储在函数环境记录中。
this:绑定,支持访问函数的上下文。
代码示例
function foo(o, p) {
let b = 1;
function bar(e) {
console.log(e);
}
bar(b);
}
foo(1, 3);- 当 foo 执行时,创建函数环境记录
- 这个记录中存储着 o,p,b,bar 的映射
foo:
Function Enviroment Record:
o: undefined
p: undefined
b: initialize
bar: <Fn>
outerEnv: Global
this: window- 当 bar 执行时,创建 bar 函数环境记录
- 这个记录中存储着 e
bar:
Function Enviroment Record:
e: undefined
outerEnv: foo Function Enviroment Record
this: window模块环境记录 Module Environment Records
感觉用的很少,这里引用下官方介绍,就不展开记录了
A Module Environment Record is a Declarative Environment Record that is used to represent the outer scope of an ECMAScript Module.
总结环境记录
- 定义标识符与 变量&函数 的关联,当代码运行到需要获取某个标识符值的时候,会从环境记录中去拿
- 当****遇到以下代码时,就会创建一个新的环境记录
- 函数声明:最开始执行的
script,以及普通的函数声明 - {}块语句
- try catch 的 catch 块
- 函数声明:最开始执行的
- 每个环境记录都有[[outerEnv]],根据 outerEnv 可以访问外部环境,形成链。当当前环境记录没有找到映射,会根据 outerEnv 从外部环境中寻找
TIP
上文提到,执行上下文中的词法环境、变量环境的本质都是环境记录,那么他们之间的关系,怎么理解,又是怎么对应的
词法环境
Identifies the Environment Record used to resolve identifier references made by code within this execution context.
标识环境记录,该环境记录被用来解析代码在此执行上下文中对标识符的引用。用于解析代码中的标识符引用
标识符解析:
- 当代码引用某个标识符(例如变量名或函数名)时,JavaScript 引擎会通过当前执行上下文的
LexicalEnvironment找到对应的 环境记录,以解析该标识符。
TIP
从 ES2015 -> ES2024, 发现在从 ES2021 开始,Lexical Environments(有空格)的概念被取消了, 把原先的 Lexical Environments 改为 Environments Record
--- 到此我才缓过来
变量环境
Identifies the Environment Record that holds bindings created by VariableStatements within this execution context.
用于标识环境记录,该环境记录保存由该执行上下文中的 VariableStatements 创建的绑定。
用于保存由
VariableStatements(变量声明语句)创建的绑定
The LexicalEnvironment and VariableEnvironment components of an execution context are always Environment Records.
执行上下文中的 LexicalEnvironment 和 VariableEnvironment 组件始终是环境记录。
明确了:就是环境记录
TIP
怎么理解
环境记录 ** 定义标识符 与 函数&变量的关联 **
词法环境 解析代码中标识符引用,如何解析?找对应的环境记录
变量环境 保存由VariableStatements(变量声明语句)创建的绑定,找对应的环境记录
那么可以理解 词法环境、变量环境 --> 环境记录 --> 找对应关系
代码辅助理解
示例 1
TIP
先 Mark 暂时只思考到这,后续境界上来持续更新
function foo() {
var a = 1;
let b = 2;
console.log(c);
if (a === 1) {
var c = 3;
let d = 4;
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
console.log(d);
}
foo();foo FunctionExecutionContext:
LexicalEnvironment: // (我理解这是一个抽象的,比环境记录还抽象,自身并不是一个环境记录)
d: DeclarativeEnvironmentRecord --- initialize
LexicalEnvironment:
b: FunctionEnvironmentRecord --- initialize
VariableEnvironment:
a: FunctionEnvironmentRecord --- undefined
c: FunctionEnvironmentRecord --- undefined
// 记录的是 标识符 变量的关联 (执行前)
foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord:
a: undefined
b: initialize
outerEnv: GlobalEnvironmentRecord
{} DeclarativeEnvironmentRecord
c: undefined
d: initialize
outerEnv: foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord我的理解:
- 当 foo 函数执行,在执行前夕,会创建 foo 函数的 FEC,在执行上下文中,词法环境、变量环境随之创建,与之对应的,函数环境记录也随之创建,所以我理解在 foo 执行前夕,创建的结构如下:
foo FunctionExecutionContext:
LexicalEnvironment:
b: initialize
VariableEnvironment: // 只是抽象,具体还得在环境记录中找
a: undefined
c: undefined // c之所以会在初始被创建,完全是因为var的声明提升,思考下等价代码
foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord:
a: undefined
b: initialize
c: undefined
outerEnv: GlobalEnvironmentRecord- 当执行到
var a = 1,会找到变量环境中的 a,进而找到函数环境记录中的 a,将值改为 1
foo FunctionExecutionContext:
LexicalEnvironment:
b: initialize
VariableEnvironment: // 只是抽象,具体还得在环境记录中找
a: 1
c: undefined // c之所以会在初始被创建,完全是因为var的声明提升,思考下等价代码
foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord:
a: 1
b: initialize
c: undefined
outerEnv: GlobalEnvironmentRecord- 继续执行到
let b = 2,会找到当前词法环境中 b,进而找到函数环境记录中的 b,将值改为 2
foo FunctionExecutionContext:
LexicalEnvironment:
b: 2
VariableEnvironment: // 只是抽象,具体还得在环境记录中找
a: 1
c: undefined // c之所以会在初始被创建,完全是因为var的声明提升,思考下等价代码
foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord:
a: 1
b: 2
c: undefined
outerEnv: GlobalEnvironmentRecord- 继续执行到
console.log(c)会找到变量环境中 c,进而找到函数环境中的 c,此时的 c 是 undefined - 继续执行遇到了块{}, 会创建一个词法环境,以及块的声明式环境记录
foo FunctionExecutionContext:
LexicalEnvironment:
d: initialize
LexicalEnvironment:
b: 2
VariableEnvironment: // 只是抽象,具体还得在环境记录中找
a: 1
c: undefined // c之所以会在初始被创建,完全是因为var的声明提升,思考下等价代码
{} DeclarativeEnvironmentRecord
d: initialize
outerEnv: foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord
foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord:
a: 1
b: 2
c: undefined
outerEnv: GlobalEnvironmentRecord- 执行到
var c = 3,找到变量环境中 c,进而找到函数环境中的 c 赋值 3
foo FunctionExecutionContext:
LexicalEnvironment:
d: initialize
LexicalEnvironment:
b: 2
VariableEnvironment: // 只是抽象,具体还得在环境记录中找
a: 1
c: 3 // c之所以会在初始被创建,完全是因为var的声明提升,思考下等价代码
{} DeclarativeEnvironmentRecord
d: initialize
outerEnv: foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord
foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord:
a: 1
b: 2
c: 3
outerEnv: GlobalEnvironmentRecord- 继续执行到
let d = 4找到当前词法环境中的 d,进而找到块的声明式环境记录中的 d,赋值为 4
foo FunctionExecutionContext:
LexicalEnvironment:
d: DeclarativeEnvironmentRecord ---> d 4
LexicalEnvironment:
b: FunctionEnvironmentRecord ---> b 2
VariableEnvironment: // 只是抽象,具体还得在环境记录中找
a: 1
c: 3 // c之所以会在初始被创建,完全是因为var的声明提升,思考下等价代码
{} DeclarativeEnvironmentRecord
d: 4
outerEnv: foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord
foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord:
a: 1
b: 2
c: 3
outerEnv: GlobalEnvironmentRecord- 继续执行到
console.log(a),a 从当前词法环境对应的环境记录中找,没找到,根据 outerEnv,再找到 FunctionEnvironmentRecord 中的 a, 打印为 1 - 继续执行到
console.log(b),会从当前词法环境对应的环境记录中寻找,没找到,会到环境记录的外层环境记录 - 函数环境记录中寻找,找到为 2 - {},执行完成后,会销毁块词法环境 以及 当时创建的块声明式环境记录
foo FunctionExecutionContext:
LexicalEnvironment:
b: FunctionEnvironmentRecord ---> b
VariableEnvironment: // 只是抽象,具体还得在环境记录中找
a: 1
c: 3 // c之所以会在初始被创建,完全是因为var的声明提升,思考下等价代码
foo FunctionEnvironmentRecord:
a: 1
b: 2
c: 3
outerEnv: GlobalEnvironmentRecord- 继续执行
console.log(d),会在当前的词法环境对应的环境记录中寻找,找不到,再去全局环境记录中寻找,找不到,报错 - 若无
console.log(d)那么执行完成后,执行上下文以及对应的环境记录都会销毁
参考:
ECMAScript 规范(2024)
ECMAScript 规范(2015)ES6
Javascript 忍者秘籍(第 2 版)
https://juejin.cn/post/7118721446615973896#heading-2
...
